Breathing
Breathing is the process of getting oxygen into the lungs and carbon dioxide out of the lungs. It allows for gas exchange to take place so that oxygen can be absorbed from the lungs into the blood and carbon dioxide is removed from the blood and breathed out from the lungs.
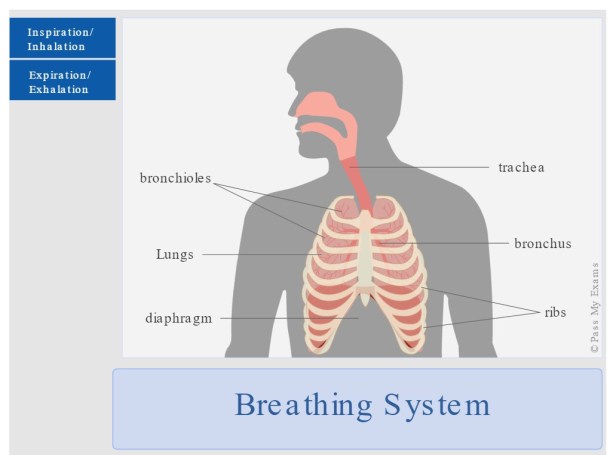
The Breathing System
When we breathe, air moves into and out of our body. There are two movements involved in the process of breathing:
✅ *Inspiration (also known as inhalation) – This is breathing air into the body.*
When we inspire:
The intercostals muscles found between the ribs contract. This raises the ribs upwards and outward expanding the ribcage diaphragm contracts and flattens, pulling downwards.
The result is that the thorax increases in volume, which in turn lowers the pressure inside it and consequently air is sucked into the lungs.
✅ *Expiration (also known as exhalation) – This is breathing air out of our body.*
When we expire:
The intercostal muscles relax. This lowers the ribs downwards and inwards. The diaphragm relaxes, moving back upwards. The result is that the thorax decreases in volume, which in turn increases the pressure inside it and consequently forces air out of the lungs.
Gas Exchange
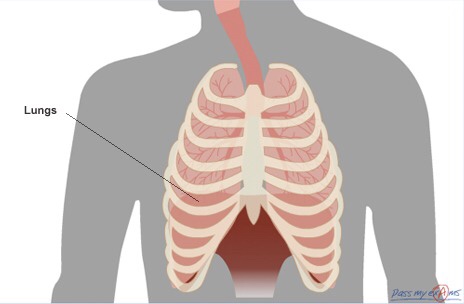
In order to see how gas exchange occurs we need to look further into the lungs. Firstly we know that air enters the body through the mouth or nose, from here it moves to the pharynx (throat), passes through the larynx (voice box) and enters the trachea. The trachea splits into two branches, *the left and right bronchus*, each bronchus divides many times into smaller branches called *bronchioles*. Each bronchiole finally leads to a bunch of tiny air sacs, called *alveoli*, which inflate during inhalation, and deflate during exhalation.
*It is at the alveoli where gas exchange takes place.*
Gas exchange is the delivery of oxygen from the lungs to the bloodstream, and the elimination of carbon dioxide from the bloodstream to the lungs and out of the body.

Air enters the body through the mouth and nose, from here it moves to the pharynx (throat), passes through the larynx (voice box) and enters the trachea.
The trachea splits into two branches, the left and right bronchus, each bronchus divides many times into smaller branches called bronchioles.
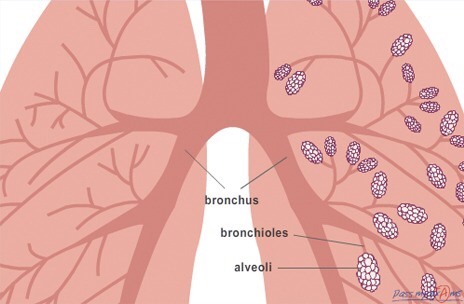
Each bronchiole finally leads to a bunch of tiny air sacs, called alveoli, which inflate during inhalation, and deflate during exhalation.
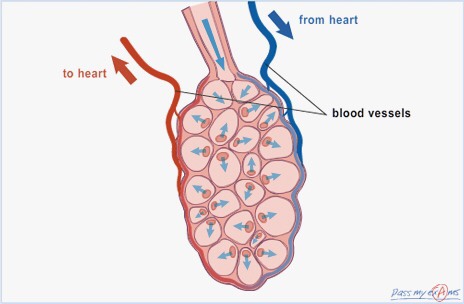
Gas exchange is the delivery of oxygen from the lungs to the bloodstream, and the elimination of carbon dioxide from the bloodstream to the lungs and out of the body. It takes place in the alveoli.
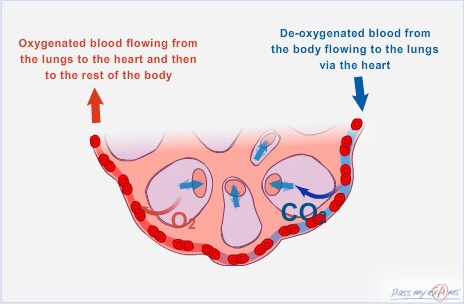
The walls of the alveoli are surrounded by a network of blood capillaries. In fact the alveoli walls share a membrane with the capillaries which allows for oxygen to diffuse through the alveoli wall and enter the bloodstream and then travel to the heart. At the same time it allows for carbon dioxide to diffuse from the bloodstream into the alveoli and exhaled out of the body. Both oxygen and carbon dioxide move from areas of high concentration to areas of lower concentration.

This website is helpful and also helps one to understand things very well before or after been taught in class.
LikeLike
Thanks very much.keep following us and share to all your friends and other students ✅…You can also WhatsApp us 0547316472
LikeLike